usp class vi vs fda
Class VI testing is aimed to certify that there are no harmful reactions or long-term bodily effects caused by chemicals that leach out of plastic materials. Pharmacopoeia USP Class VI outlines requirements for system toxicity and intracutaneous toxicity for these cleaner compounds.
Pharmacopeia USP a non-profit organization whose standards inform decision-making at the US.
. USP Class VI refers to a set of biocompatibility testing requirements from the US. There are six classes VI being the most rigorous. That being said if you cant get an ISO 10993 compliant material often because the material simply hasnt been tested using a USP Class VI material is a less risky option.
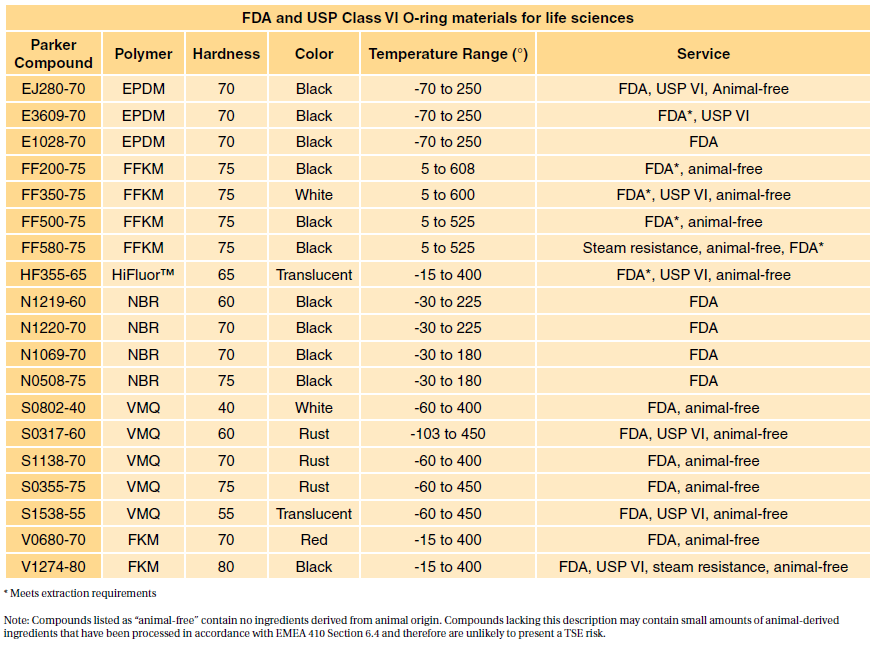
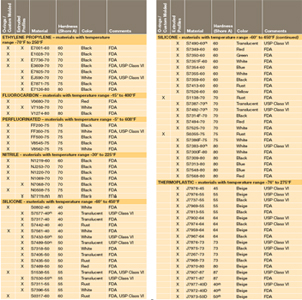
Extraction-360 cm2 05 mm thick 180 cm2 ³ 05 mm thick or 12 g Implant 12 pieces at 1mm x 1mm x 10 mm. Extraction- 480 cm2. Table 1 shows our standard programme FDA compliant com-pounds which can be produced in a few days.
USP Class testing is one of the most common methods of testing to determine bio-compatibility of materials. Materials that meet USP Class VI standards generally ensure a high quality level and better acceptance with the FDA and USDA because the materials are believed to substantially reduce the risk of causing harm to patients from reaction to a toxic material. The USP Class VI compounds must be made from ingredients with clear histories of biocompatibility that meet tighter requirements for leachates.
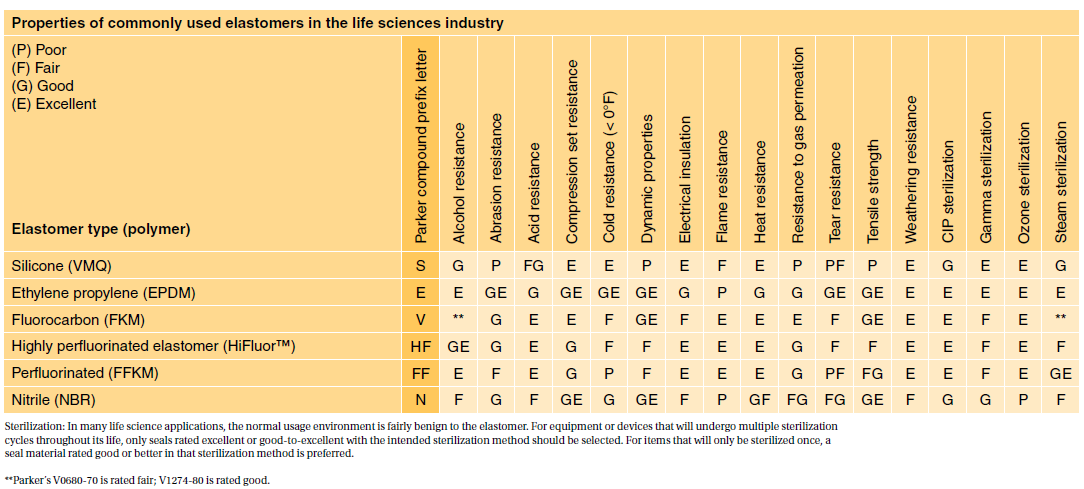
Sil 714001 USP class VI Silicone 1 70 Yes transl. In 1995 the FDA adopted ISO 10993 as its biocompatibility approach. Most applications are fairly benign to elastomers.
27 rows The US. This is their current stance today. The USP Class VI compounds must be made from ingredients with clear histories of biocompatibility that meet tighter requirements for leachates.
USP Class VI materials EPDM Silicone Fluorocarbon and Perfluoroelastomer 24 materials which are compliant to FDA 21 CF R1772600. USP Class VI. Food and Drug Administration FDA.
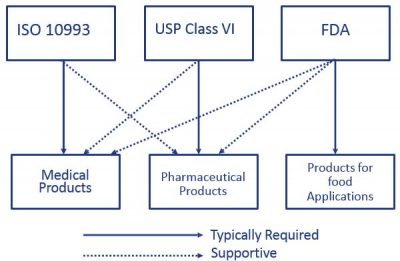
Both ISO 10993 and USP Class VI define testing requirements for biocompatibility the ability of a material to perform a desired function without causing adverse effects on. USP Class VI Regiment Irritation Systemic Injection Implantation 1 week Biological Evaluation Plan BEP Manufacturers need to. In 1988 in vitro tests were explored and USP concluded that in vitro.
To begin the USA food and Drug Administration FDA places regulations on three different types of food additives- direct secondary direct and indirect food additives. Some medical silicones must meet USP Class VI FDA CFR 21 1772600 and RoHS requirements. RoHS a European Union Directive restricts the use of certain substances but manufacturers also need to know whether all the ingredients in a medical silicone are made of compliant materials.
USP Class VI and FDA White List Silicone and Organic Elastomer Compounds for. By adhering to the standards of the USP and the FDA Class VI O-rings are much better suited for use in these industries for both the continued efficient operation of the plant and for the safety of the consumer or user of the products that are being made. PRODUCT TITLE AND IMPLICATIONS FOR CONTAINER AND CARTON.
Most importantly use of Class VI certified materials substantially reduces the risk of causing harm or increased stress to a patient from reaction to a toxic material. Up-to-date materials manufacturers provide both USP and ISO 10993 test data to support both pharma and device customers. 1965 USP XVII introduced Biological TestsPlastics Containers section was added and made official in the Compendium.
Sil 714002 USP class VI Silicone 1 70 Yes transl. The USP-FDA relationship dates back to the 1906 Pure Food and Drug Act which deemed the United States Pharmacopeia and the National Formulary official compendia under federal law. Moulded O-rings class 1 less than 10 furnace black These can be produced in all possible dimensions up to diameter 1400 mm internal.
How USP and FDA Work Together. For most patient-contact applications a material that meets US Pharmacopeia USP Class VI andor ISO 109933 will be required. USP Class VI Permanent USP Class V Prolonged USP Class IV Limited Blood Path Indirect Mucosal Surfaces Limited USP Class I USP Class III Permanent USP Class V TissueBoneDentin Communicating USP Class IV Limited Prolonged Surface Devices External Communication Devices.
For this reason the FDA provides a standard 21 CFR1772600 defining allowable rubber compound ingredients and extractibles based on toxicity and carcinogenicity. USP class qualification no longer plays any role in medical device materials evaluation. USP and FDA maintain official contact through a number of established channels.
USP-FDA Shared History and Mission. 480 cm2 05 mm thick 240 cm2 ³ 05 mm thick or 16 g. One standard often overlooked but usually published alongside USP Class VI is FDA 21 CFR 1772600.
The guidance memo wasis G95-1. Specially formulated for long term sealing. US FDA guidance document Use of International Standard ISO 10993-1 Biological evaluation of medical devices.
USP Class Testing standards are determined by the United States. There may be some confusion between FDA USP Class VI and FDA food grade materials. Specifically USP publishes test instructions for the plastics polymers and elastomers that are used in medical devices and surgical equipment.
Typical applications for our FDA NSF 51 USDA materials are disposable medical devices surgical instruments and medical fluid dispensing components as well as a wide variety of food and beverage. Plastics were assigned Class I-VI based on the biological in vivo testing systemic injection intra-cutaneous and implantation tests. USP Class VI Testing is only one standard of biocompatibility however.
FDA food-grade rubber materials typically comply with FDA 21. It generally ensures a high quality level and better acceptance with the FDA and USDA. 87 the United States Pharmacopeia USP drug product monograph title for that drug product.
USP Class VI Testing is only one standard of biocompatibility however. Class VI materials which were discussed earlier are tested according to the above protocols. The FDA requires testing of finished devices however the demonstration of biocompatibility of materials according to USP Class VI standards is provided as an aid to device manufacturers in their material selection process.
While it is possible a USP Class VI material could also be ISO 10993 compliant its not a given and USP Class VI alone is not sufficient for adherence to ISO 10993. Typical applications for our FDA NSF 51 USDA materials are disposable medical.

Understanding Food Grade Vs Biocompatibility For Medical Device Materials Medical Product Outsourcing

Fda Usda Nsf51 Usp Class Vi Compliant Seals Products

Fda And Usp Class Vi O Rings Guide 2020 Nes
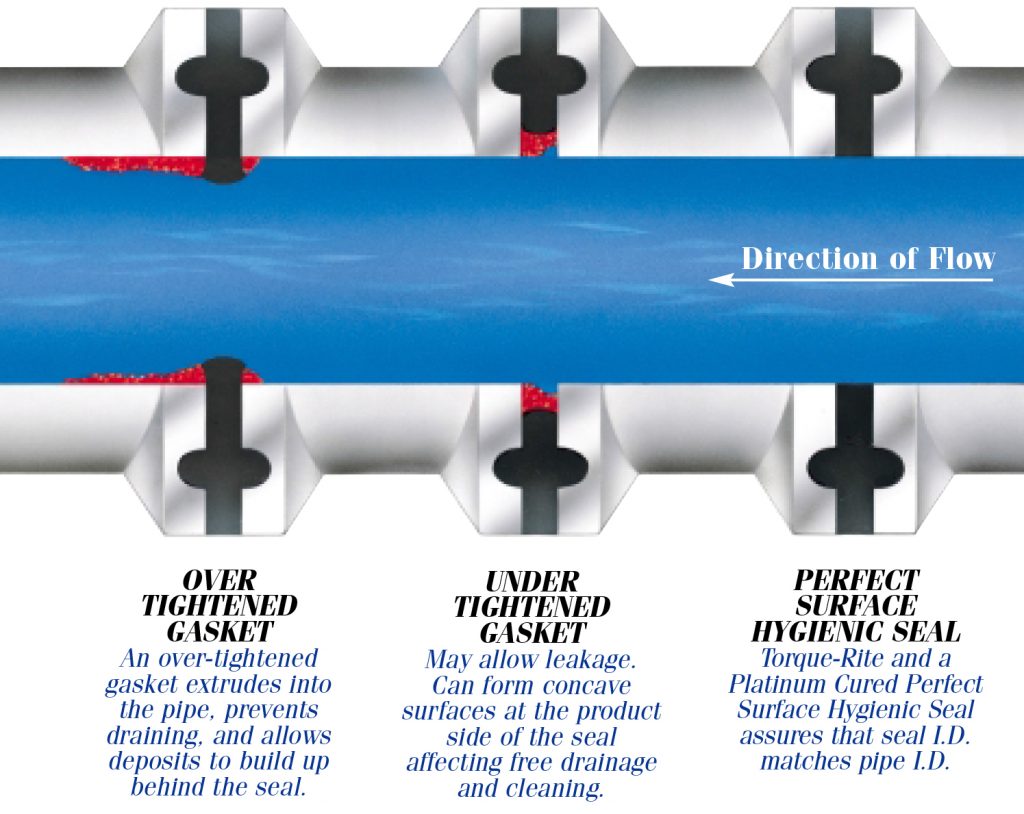
Standard Fda And Usp Class Vi Compliant Materials For All Types Of Hygienic Connections Repassa

Usp Class Vi Foster Corporation

Iso 10993 Vs Usp Class Vi Medical Molding And Bicompatible Rubber The Rubber Group